A Decade of Cybersecurity in Fintech
Digital finance has undergone a dramatic transformation over the past 10 years. Starting in the mid-2010s with the rise of mobile banking, peer-to-peer payments, and blockchain platforms, financial services rapidly embraced digital innovation. This evolution brought efficiency and convenience, while also exposing new security vulnerabilities. Between 2015 and 2025, cybersecurity in financial technology (fintech) shifted from basic firewalls and antivirus tools to advanced threat detection, encryption, and regulatory compliance frameworks designed to safeguard complex, high-speed financial systems. As fintech has grown into an integral part of global finance, cybersecurity has evolved from a niche IT concern to a strategic priority on the boardroom agenda.
Fintech’s Evolution and Corresponding Cybersecurity Solutions
From digital banking to open finance, fintech has progressed through several key phases:
- Mobile & Online Banking (2015–2020): Early adoption of digital services saw basic fraud defenses and two-factor authentication implemented across platforms.
- API-Driven Ecosystems (2020–2023): Fintech platforms began using APIs to interconnect services, increasing integration but also creating new attack surfaces.
- AI & Blockchain Adoption (2024–2026): Financial services now leverage automation, machine learning, and decentralized ledgers, expanding both capability and complexity.
These advancements demanded a corresponding evolution in fintech cybersecurity frameworks:
- Zero-trust architectures to prevent unauthorized access.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and biometrics to strengthen identity safeguards.
- Real-time threat intelligence and response automation powered by AI.
- Compliance automation (RegTech) to meet stringent regulations across global jurisdictions.
Why Cybersecurity is Vital in Fintech
Cybercrime’s Rising Impact underscores why robust fintech cybersecurity can’t be overstated. Consider these concerning trends in recent years:
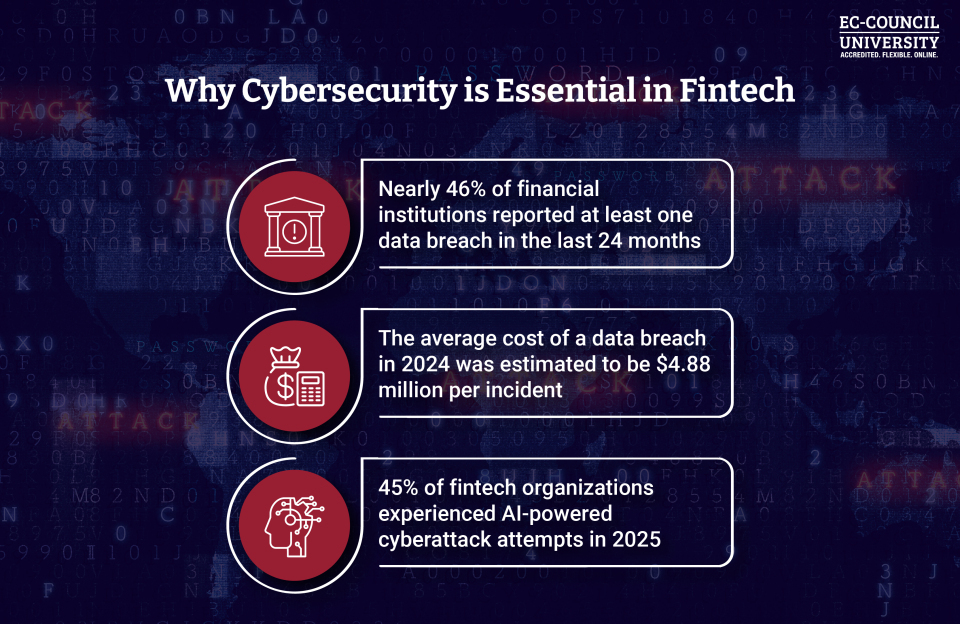
- Nearly 46% of financial institutions reported at least one data breach in the last 24 months, with 65% experiencing ransomware attacks in 2024 alone. (Source: DigitalDefynd Education)
- The average cost of a data breach in 2024 was estimated to be $4.88 million per incident. (Source: IBM)
- The global financial sector is the most vulnerable to AI-driven cybercrime, with 45% of organizations in this space experiencing AI-powered cyberattack attempts in 2025. (Source: Axios)
Notable Cyberattacks on Financial Institutions
- SitusAMC Vendor Breach
In late 2025, SitusAMC, a mortgage services technology provider, suffered a cyberattack that exposed data from over 100 financial institutions, including prominent U.S. banks such as JPMorgan Chase, Citibank, and Morgan Stanley. - JPMorgan Chase Breach
Although older, the 2014 JPMorgan Chase data breach remains one of the most significant financial sector attacks in history, affecting more than 83 million customer accounts. This event helped catalyze heightened cybersecurity investments across global banks. - State-Level Attacks on Banking Systems
In August 2024, a coordinated attack against Iranian banks by cyber actors disrupted ATM services and forced temporary shutdowns, illustrating how financial infrastructure can be targeted on a massive scale.
AI in Fintech Cybersecurity: The Benefits and Downsides
Enhancing Fintech Cybersecurity with AI
AI gives fintech firms the ability to stay ahead of cybercriminals through:
- Real-Time Fraud Detection: AI analyzes millions of transactions instantly, identifying unusual behavior such as abnormal spending, location changes, or device mismatches to prevent fraud in real-time.
- Adaptive Threat Intelligence: Machine learning continuously learns from new attack patterns, allowing security systems to evolve automatically as cybercriminal tactics change.
- Behavioral Biometrics: AI continuously monitors user behavior such as typing speed, navigation patterns, and touch dynamics to verify identity and detect account takeovers.
- Anomaly and Insider Threat Detection: AI correlates activity across systems to detect subtle anomalies, insider threats, and coordinated attacks that traditional tools may miss.
- Automated Incident Response: When integrated with security platforms, AI can automatically block malicious activity, isolate compromised accounts, and trigger additional authentication steps.
- Predictive Risk Scoring: AI assigns dynamic risk scores to users and transactions, enabling fintech platforms to apply stronger controls only when risk is elevated.
- Enhanced AML and KYC Monitoring: Machine learning improves anti-money laundering and customer verification by identifying hidden transaction patterns and suspicious financial networks.
- Reduced Analyst Workload: AI filters out false positives and prioritizes high-risk alerts, enabling cybersecurity teams to focus on complex investigations and threat hunting.
AI-Powered Threats to Fintech Cybersecurity
AI can also empower cybercriminals by maximizing the effectiveness of their attacks through:
- AI-Generated Phishing: Cybercriminals use AI to create highly personalized, realistic phishing emails that mimic banks, fintech apps, and executives, increasing the success rates of fraud.
- Deepfake Scams: AI-driven voice and video deepfakes enable identity impersonation, fraudulent transaction approvals, and social engineering attacks against customers and employees.
- Automated Cyberattacks: AI enables attackers to automate reconnaissance, vulnerability scanning, and exploitation, allowing for continuous and adaptive attacks on a massive scale.
- Credential Stuffing and Account Takeovers: Machine learning optimizes credential-stuffing attacks by predicting password patterns and identifying valid logins faster.
- Synthetic Identity Fraud: AI helps create realistic fake identities that bypass basic KYC checks, open unauthorized accounts, and commit large-scale financial fraud.
- Evasion of Security Controls: AI-powered malware dynamically changes behavior to avoid detection by traditional security tools.
- Attacker–Defender Imbalance: Open-source AI tools enable cybercriminals to innovate quickly, often outpacing defensive updates in regulated fintech environments.
- Rising Financial Impact: AI-enabled fraud increases attack speed, scale, and financial losses, forcing fintech firms to adopt more advanced defenses.
Best Fintech Cybersecurity Practices
| Practice | Purpose | Who It Benefits |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Prevents unauthorized access | Individuals and organizations |
| Zero-Trust Architecture | Restricts implicit trust | Organizations |
| Regular Software Patching | Mitigates known vulnerabilities | Organizations |
| Employee Cyber Awareness Training | Reduces human-factor risks | Individuals and organizations |
| Secure API Management | Protects interconnected services | Organizations |
| Real-Time Monitoring & AI-Based Detection | Rapid threat identification | Organizations |
| Strong Password Security | Protects personal accounts | Individuals |
| Incident Response Planning | A ready response reduces damage | Organizations |
| Encryption of Sensitive Data | Protects data at rest and in transit | Individuals and organizations |
| Secure Cloud Configuration & Backups | Ensures continuity and recovery | Organizations |
Future Fintech Trends and Cybersecurity Implications
Here are the top 4 trends to expect in fintech, and what they mean for cybersecurity:
- Quantum Computing and Cryptography
Advances in quantum computing will challenge existing encryption methods, necessitating the development of quantum-resistant cryptographic solutions to maintain security. - Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Expansio
As DeFi grows, so will the complexity of smart contract attacks and cross-chain vulnerabilities. - Regulatory Frameworks
Emerging global cybersecurity regulations, such as the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), will raise minimum security standards across the fintech sector. - AI-Driven Security and Threats
AI will remain a double-edged sword, helping defenders while training attackers. Security teams must invest in adaptive AI defenses and human oversight.
Top 10 Cybersecurity Job Roles in the U.S. Financial Sector (2026)
| Job Role | Approx. Average Salary |
| Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) | $250,000+ |
| Security Architect | $150,000–$230,000 |
| Cloud Security Engineer | $173,000–$228,000 |
| Principal Security Engineer | $182,000–$253,000 |
| Cybersecurity Analyst | $102,000–$154,000 |
| Cybersecurity Engineer | ~$125,000 |
| Identity & Access Management Specialist | ~$133,000 |
| Network Security Engineer | $113,000–$140,000 |
| Incident Responder | ~$65,000–$85,000 |
| Application Security Engineer | ~$117,000 |
(Salary ranges reflect industry data for cybersecurity roles relevant to the fintech and financial services sectors)
The Educational Imperative for Fintech Cybersecurity
As fintech accelerates digital transformation across the financial services sector, cybersecurity risks are growing in scale, sophistication, and impact. Securing digital payments, cloud-based platforms, open banking APIs, and AI-driven financial systems requires skilled professionals with hands-on expertise and a strong understanding of regulated environments. This makes cybersecurity education essential.
EC-Council University (ECCU) prepares individuals for in-demand fintech cybersecurity roles through industry-aligned degrees and globally recognized certifications. Our bachelor’s and master’s degrees in cybersecurity provide a strong foundation in secure application development, cloud and API security, digital forensics, ethical hacking, network security, governance, risk, and compliance (GRC), and much more. ECCU’s certification programs further enhance job readiness by delivering practical, role-specific skills. Cybersecurity certifications such as Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), Certified Cloud Security Engineer (CCSE), Certified SOC Analyst (CSA), and Computer Hacking Forensic Investigator (CHFI) closely align with the real-world security challenges faced by fintech organizations.
As artificial intelligence reshapes fintech operations, ECCU integrates AI security concepts into the curriculum, enabling professionals to defend against AI-enabled fraud while securing automated financial systems responsibly. Through rigorous academics, hands-on learning, and respected credentials, EC-Council University equips cybersecurity professionals to protect modern financial ecosystems and stay ahead of evolving threats.
Want to know more?
Frequently Asked Questions About Fintech Cybersecurity
AI enhances threat detection but also enables sophisticated attacks, such as AI-powered phishing, making both defense and risk management more complex.
Threats include ransomware, phishing, credential stuffing, API attacks, and vulnerabilities in third-party applications and services.
Zero trust assumes no implicit trust; every access request must be verified to reduce unauthorized access risk.
Key skills include threat analysis, secure coding, cloud security, identity management, incident response, and knowledge of relevant regulations and standards.







