In 2026, the cyber threat landscape continues to evolve rapidly. Cyberattacks continue to be driven by cutting-edge technology and the increasing sophistication of cybercriminal ecosystems. To provide a perspective of the current scenario, in the U.S., ransomware attacks have significantly increased by 150%, making the country a global epicenter of ransomware attacks, far ahead of Canada and the UK.
For businesses, governments, and professionals across the United States, understanding which industries are most at risk and how to prepare is not just strategic but essential for survival.
Looking back at the 2025 industry cyber threat analysis, the patterns and risks are expected to persist and dominate in 2026.
2025 Industry Cyber Threat Analysis-Lessons Learnt
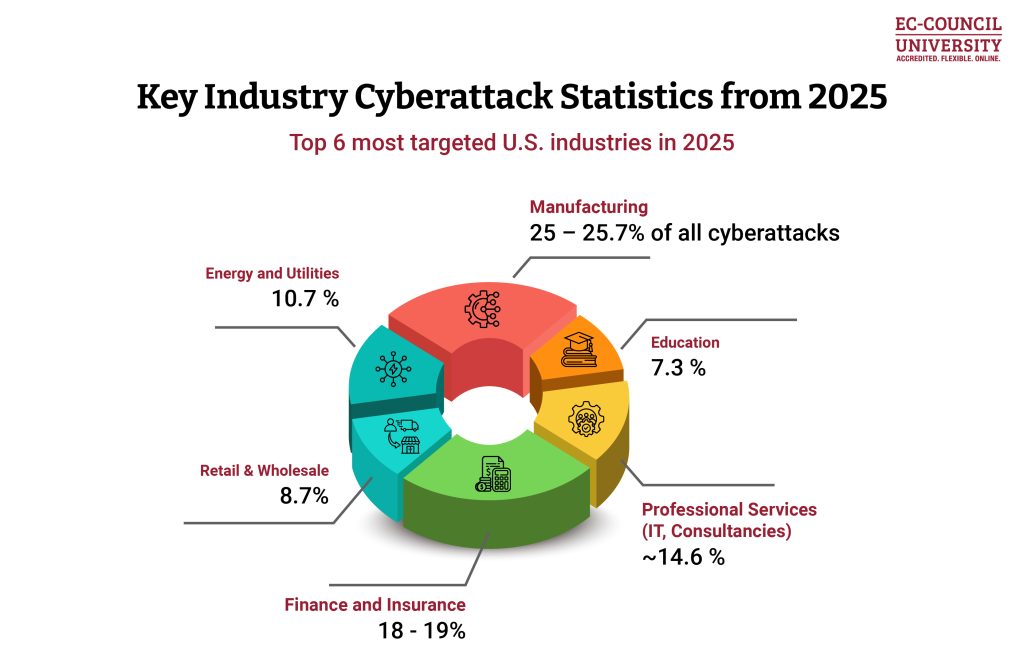
Note: Percentages may vary slightly between sources; however, the following figures reflect the most commonly reported estimates based on industry analyses.
Most Targeted Industries in the U.S. (2025 Data)
1. Manufacturing
Overview: The most targeted sector for the fourth consecutive year. Manufacturing accounted for the highest share of U.S. ransomware attacks in 2025, with over 1,000 confirmed incidents.
Notable 2025 U.S. Cyberattacks and Breaches
- The Crystal D ransomware attack in March 2025 disrupted communications and deliveries; LockBit claimed responsibility.
- The JPW Industry ransomware attack in April 2025 led to the leakage of personal data and operational disruptions.
- The Nevro medical equipment manufacturer suffered a data breach in April 2025, resulting in a significant exposure of personal data.
Industry Impact
- Production halts and supply chain delays
- Financial losses from downtime and ransom payments
- Safety risks from OT/ICS compromise
- Theft of intellectual property
- Regulatory and compliance exposure
2. Healthcare
Overview: Nearly 93% of U.S. healthcare organizations reported attacks in 2024, with trends continuing in 2025 due to high-value patient data and operational urgency.
Notable 2025 U.S. Cyberattacks and Breaches:
- A ransomware breach at Covenant Health exposed sensitive information for nearly 478,000 patients.
- The UnitedHealth/Change Healthcare breach, the most significant healthcare data breach in U.S. history, affected approximately 192.7 million individuals.
- Attack on DaVita — a major U.S. dialysis provider, exposed data tied to over 900,000 individuals.
Industry impact:
- Risk of identity theft and fraud for patients
- Disrupted claims processing and operations
- Compliance and regulatory penalties
3. Finance & Insurance
Overview: Persistent credential theft, phishing, and financial fraud make this sector highly attractive. Average breach costs reach multi-million dollars.
Notable 2025 U.S. Cyberattacks and Breaches
- The Allianz Life Insurance breach in July 2025 resulted in the exposure of 1.4 million customer and employee records due to a vendor compromise.
- Aflac reported a major breach in June 2025, which resulted in the exposure of sensitive customer information of millions of policyholders.
Industry impact:
- Massive data compromise (accounts, transaction histories)
- Identity fraud and money laundering
- Regulatory compliance pressure
4. Education & Public Institutions
Overview: This is the fourth-most targeted sector, often lacking funds for defense, and open-access systems increase vulnerability. Ransomware attacks rose 23% YoY in H1 2025.
Notable 2025 U.S. Cyberattacks and Breaches
- A 2025 breach of the PowerSchool Support Portal affected over 60 million students and 10 million teachers across the U.S. The stolen data included personal information, and the attackers demanded $2.85 million in bitcoin as ransom.
- In August 2025, a data breach at the University of St. Thomas resulted in over 630,000 sensitive files from the university’s network accessed and leaked on the dark web.
Industry Impact
- Widespread exposure of student and educator records
- System outages, disrupting LMS, email, and portals
- Operational disruption and class suspension
- High remediation costs and loss of trust
5. Government & Critical Infrastructure
Overview: Government agencies and critical services, including energy and utilities, continued to face significant pressure from ransomware and data breaches. The industry was consistently the most targeted due to the high-value data, operational criticality, and easy exposure, and was vulnerable to ransomware and phishing attacks.
Notable 2025 U.S. Cyberattacks and Breaches
- The Paul Municipal Systems Attack in July 2025 was a significant, coordinated cyberattack that disrupted municipal systems for several days, prompting a declaration of a state of emergency.
- A Microsoft SharePoint Cyber Intrusion in July 2025 significantly affected at least 400 U.S. federal and state government organizations.
Industry Impact
- Operational disruption of public services
- Exposure of sensitive government data
- National security and intelligence risk
- High mitigation costs and IT resource strain
Different Types of Cyber Attacks Across Industry in 2025

- Ransomware remains the top attack vector, which spiked dramatically year over year, accounting for a large share of extortion and data theft incidents.
- Phishing (including AI-enhanced) was cited as the origin of ~91% of successful cyberattacks across various sectors.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) and credential theft remain the leading causes of finance and service-sector breaches.
- Supply chain and third-party attacks increased significantly as attackers looked to pivot through trusted partners.
- Data exfiltration (stealing data without encryption) grew as a ransomware tactic evolved.
Cyber Threat Landscape of the US In 2026: What Organizations Must Prepare For?
Top 6 Cyber Attack Vulnerable Industries in 2026 and Why Hackers Are Targeting Them
Based on evolving threat patterns, incident data from 2025, and emerging cyberattack techniques, the following industries are projected to be the most vulnerable in 2026:
1.Healthcare sector: High data value + urgent operational requirements
The healthcare sector remains the most vulnerable due to the combination of high-value patient data and critical operational dependency.
- Sensitive patient data: Medical records, insurance information, and research IP fetch premium prices on the dark web.
- Urgent operational dependency: Hospitals and clinics must remain online to treat patients; attackers exploit this urgency with ransomware.
- Regulatory fines risk: HIPAA non-compliance following breaches can lead to substantial penalties, increasing pressure to pay ransoms.
2. Manufacturing & Industrial sector: Legacy systems, IoT exposure
Manufacturing environments are increasingly targeted due to legacy systems and expanding IoT exposure.
- Mixed IT/OT environments: Legacy industrial control systems are often unpatched and exposed, providing easy entry points.
- Production line disruption = high leverage: Attackers can halt assembly lines, resulting in significant financial and reputational damage.
- Supply chain dependencies: Exploiting one manufacturer can create a ripple effect, affecting multiple partners, amplifying the impact.
3. Financial Services & Insurance – Rich data + financial leverage
Financial institutions remain attractive targets because of direct monetization opportunities.
- High-value financial data: Data such as credit card information, bank accounts, and insurance claims, can be directly monetized.
- Immediate leverage for extortion: Attackers can demand a ransom, knowing that organizations prioritize uninterrupted access to their financial systems.
- Complex ecosystem of vendors and APIs: Opens multiple attack vectors for data exfiltration and account takeover.
4. Government & Public Sector – State-oriented threats
Government agencies face sustained pressure from ransomware and nation-state actors.
- Nation-state interest: Sensitive information, law enforcement intelligence, and public data make these agencies prime targets.
- Critical service disruption: Ransomware or sabotage can affect millions, giving attackers leverage or geopolitical advantage.
- Legacy and widely distributed systems: Multiple networks across federal, state, and local agencies increase exploitable surface area.
5. Education & Research Institutions – Weaker defenses + valuable research
Educational institutions are increasingly targeted due to weak defenses and valuable data.
- Large stores of PII: Student and faculty records are a rich source for identity theft.
- Valuable intellectual property: Research data, especially in medicine, tech, and defense-adjacent fields, can be monetized or sold.
- Lower cybersecurity maturity: Budget and expertise constraints make these institutions more vulnerable to breaches than corporate targets.
6. Energy, Utilities & Critical Infrastructure – National Risk Impact
Critical infrastructure represents a national-level risk when compromised.
- Strategic and systemic importance: Disruption can affect millions, creating a state of emergency.
- OT/SCADA vulnerabilities: Industrial control systems often lack modern security measures, exposing critical processes to risk.
- High-profile geopolitical leverage: Nation-state or ideologically motivated attackers target energy and utilities to build pressure tactics.
Attackers will focus on these industries because data value, operational dependency, weak defenses, and potential leverage converge, making them high-reward, high-impact targets in 2026.
2026 Cyber Attack Trends Shaping the Future of Digital Risk and Defense
The 2026 cyberattack trends reflect a fundamental shift with attackers exploiting trust, identity, and automation rather than just technical vulnerabilities. Below are the trends redefining digital risk across U.S. industries.

1. AI Deepfake Attacks
AI-powered deepfakes are transforming social engineering techniques. AI is no longer just a cybersecurity tool but also a weapon. Deepfake technology enables attackers to generate realistic voice, video, and written communications to impersonate executives and trusted leaders. During the 2025 holiday season, deepfakes were responsible for approximately 30% of fraud attempts against major U.S. retailers.
Industry Impact
- Financial Services: Fraudulent wire transfers and account manipulation
- Healthcare: Unauthorized system changes and data access
- Corporate Enterprises: Business Email Compromise (BEC) at scale
Learn Whether AI in Cybersecurity Is A Friend or Foe?
2. Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)
Ransomware remains the most disruptive cyber threat in the U.S., which is fueled by the rapid growth of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS). These platforms enable even low-skilled attackers to launch high-impact attacks using pre-built tools, dashboards, and payment portals. In 2025, approximately 61% of all ransomware attacks utilized RaaS infrastructure, allowing even small threat actors to launch large-scale campaigns. Manufacturing, healthcare, and local governments continue to be prime targets, where downtime directly impacts safety, revenue, and public trust.
Industry Impact
- Manufacturing: Production shutdowns and supply chain delays
- Healthcare: Disrupted care delivery and patient data exposure
- Public Sector: Service outages and operational paralysis
3. AI-Enabled Phishing & Social Engineering
Phishing remains the leading cause of initial compromise in U.S. organizations, especially in the finance, education, and professional services sectors. Phishing has evolved far beyond the use of generic emails. In 2026, attackers will utilize AI to analyze job roles, communication styles, and publicly available data to craft highly personalized messages that evade traditional defenses. This trend is displacing older forms of social engineering and increasing the overall volume of attacks.
Industry Impact
- Education: Credential theft and student data breaches
- Professional Services: Client data exposure
- Finance: Account takeovers and fraud
4. Autonomous Malware and Self-Evolving Attacks
One of the most concerning trends of 2026 is the rise of autonomous malware—self-learning malicious code that can modify its behavior in real-time to evade detection. These attacks significantly increase dwell time, allowing attackers to move laterally across enterprise environments before triggering alerts.
Industry Impact
- Technology: Intellectual property theft
- Critical Infrastructure: Persistent system compromise
- Large Enterprises: Long-term undetected breaches
5. Supply Chain and Third-Party Exploitation
Attackers increasingly target vendors, suppliers, and managed service providers to gain access to larger organizations. In the U.S., a single compromised third party can expose dozens of downstream entities.
Industry Impact
- Healthcare: Vendor-related data breaches
- Manufacturing: Supplier compromise
- Government: Cascading infrastructure risk
6. Cloud and Identity-Based Attacks
As cloud adoption becomes increasingly popular, attackers are shifting their focus from infrastructure exploits to identity abuse. Compromised credentials, excessive permissions, and token hijacking now account for a large share of breaches.
Industry Impact
- SaaS & Tech: Unauthorized data access
- Finance: Identity-based fraud
- Enterprises: Lateral movement across cloud environments
How Organizations Can Stay Secure in 2026
1. Invest in Skilled Cyber Talent
Training and education are more critical than ever. Professionals with advanced knowledge in Cybersecurity, AI security, and risk management are in high demand. Programs such as EC-Council University’s cybersecurity degrees — including Bachelor’s and Master’s degrees in Cybersecurity and specialized tracks in ethical hacking, network defense, and digital forensics — equip students with industry-aligned skills tailored to defend modern digital ecosystems.
2. Adopt Zero-Trust and AI-Driven Defenses
Legacy perimeter-based models are today obsolete. Adopting zero-trust architecture, AI-driven monitoring, and automation dramatically reduces risk and detection time.
Read Why Zero Trust Architect Is a Business Imperative
3. Continuous Learning & Certification
Cyber threats evolve quickly, and so must professionals. To tackle these evolving threats, they must pursue ongoing training, cybersecurity courses, and certifications that teach skills for identifying and responding to emerging threats, such as AI-generated attacks and complex ransomware variants.
Collaboration Across Sectors
Discover How To Stay Ahead of Raas Attack
Conclusion: Thriving Amid Cyber Risk in 2026
Cyber threats in 2026 will be much more sophisticated, automated, and intelligent, but they are not unbeatable. Organizations that invest in skilled professionals, modern defenses, and continuous learning will not only withstand attacks but also gain a competitive edge. For students and professionals, future-focused cybersecurity education, such as industry-aligned degree programs offered by EC-Council University, can be a decisive step toward building resilient careers and protecting the industries that power the U.S. economy.







